Magma And Granite Geological Process

Granite is an igneous rock that forms when magma cools relatively slowly underground.
Magma and granite geological process. Modelling shows that granite diapirism is slow and inefficient and there is little evidence of it in the geological record. It is usually composed primarily of the minerals quartz feldspar and mica. In this process existing rocks melt allowing the magma formed to be more felsic and less mafic than the pre. Variations in the lithology age and the grade of meta morphism prompted to divide the dc into the western dharwar craton wdc and the edc.
Consider how granite changes form. Shale the correct answer is a basalt review. Other articles where granitic magma is discussed. Granite has a felsic composition and is more common in recent geologic time in contrast to earth s ultramafic ancient igneous history.
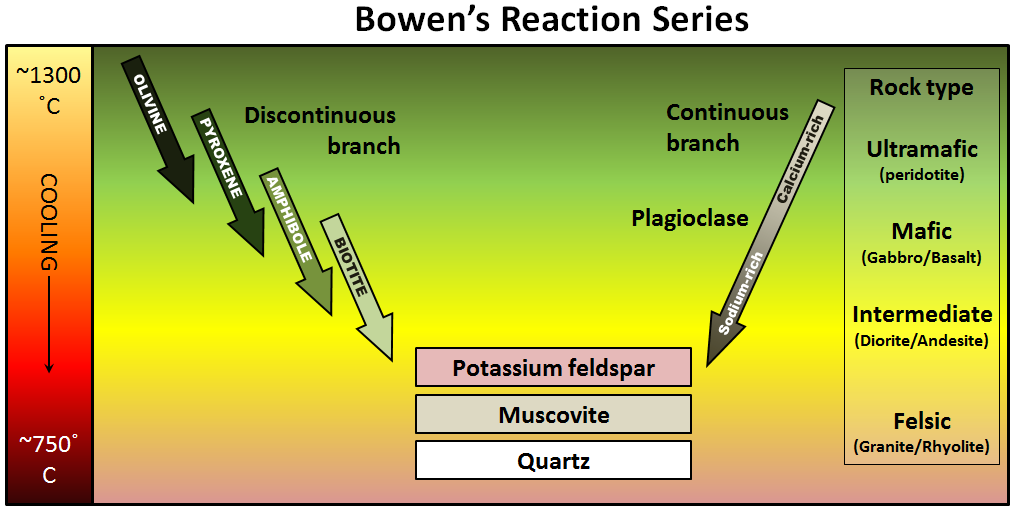
The sequence in which minerals crystallize from a magma is known as the bowen reaction series figure 3 10 and who was bowen. The host granite reveal about the magma mixing mingling environment. The granitic melt segregates into veins shears and dykes eventually forming larger feeder dykes that transport the magma rapidly upward to the emplacement sites. Granite is composed mainly of quartz and feldspar with minor amounts of mica amphiboles and other minerals this mineral composition usually gives granite a red pink gray or white color with dark mineral.
Weathering and erosion you answered correctly. Granitic or rhyolitic magmas and andesitic magmas are generated at convergent plate boundaries where the oceanic lithosphere the outer layer of earth composed of the crust and upper mantle is subducted so that its edge is positioned below the edge of the continental plate or. Geologic provinces with the shield orange and platform pink comprising the craton the stable interior of continents. This explains why a cooling magma can have some crystals within it and yet remain predominantly liquid.
It forms from the slow crystallization of magma below earth s surface. The geological efficacy of this compaction process is completely uncertain. Which geologic process is illustrated in this animation. Heat and pressure c.
Partial melting also occurs as existing crustal rocks melt in the presence of heat from magmas. Felsic rocks are less dense than mafic and ultramafic rocks and thus they tend to escape subduction whereas basaltic or gabbroic rocks tend to sink into the mantle beneath the granitic rocks of the continental cratons. Geology of study area dharwar craton dc is one of the largest cratonic blocks of peninsular india figure 1a. Types of rocks 5.
When granite is subjected to intense heat and pressure it changes into a metamorphic rock called gneiss. Iv 1 3 ascent and collection of small volumes of liquid buoyant ascent of small centimetre sized pockets of melt is possible is the viscosity of the country rocks is low enough fyfe 1970.